In this article we talk about desktop virtualization, what it, its benefits and best practices.
Desktop Virtualization is a technology where users access a device which is running at a remote location. The system will run in the cloud but the interface, i.e., desktop screen, keyboard and mouse are available to him via the network. An immediate benefit to this is that users can work on multiple computers simultaneously.
Table of Contents
What is Desktop Virtualization?
Desktop virtualization is a technology that allows you to access your PC or computer remotely in the cloud. In a nutshell, your computer is located somewhere in the cloud while your monitor, keyboard and mouse / pointing device are in front of you. You use a network (internet) to access and work on your remotely located computer, basically you access it remotely. That is an example of desktop virtualization.
If you think about it, you also access websites and apps remotely using devices like browsers and phones. People use SSH to access Linux servers remotely. But just having remote access is not ‘desktop virtualization’, but is a component which must be present for desktop virtualization to function.
In technical terms, desktop virtualization separates the desktop environment—comprising the operating system, applications, and user data—from the physical device it traditionally resides on. By virtualizing the desktop, users gain the ability to access their workspace remotely, providing a seamless computing experience that transcends geographic and hardware limitations. This means that whether you’re using a laptop, tablet, or even a smartphone, you can connect to your virtual desktop as long as you have network access.
By hosting the desktop environment on a centralized server, desktop virtualization allows centralized management of the virtualized computer systems, and better security. Organizations leverage this capability to enhance productivity, streamline IT operations, and enable remote work.
The operating system also plays a crucial role in desktop virtualization. Virtualization solutions rely on hypervisors or other software that manage and allocate resources between the host machine and virtual environments, allowing multiple virtual desktops to operate concurrently.
How Does Desktop Virtualization Work?
Desktop virtualization functions by hosting the desktop operating system on a centralized server, which acts as the backbone of the entire virtual infrastructure. Instead of being tied to a single physical machine, the user’s desktop is transformed into a virtual instance that resides on a server, enabling flexibility and scalability. This centralized approach allows organizations to manage multiple desktop environments efficiently, reducing the overhead associated with maintaining individual physical devices.
With desktop virtualization, multiple users can access their personalized virtual desktops simultaneously, even though these desktops are running on the same underlying server. Each user’s virtual environment is isolated, ensuring privacy and security while maintaining system performance. This setup not only optimizes resource utilization but also enhances the ability to scale the system to meet growing demands.
Accessing a virtual desktop is straightforward and can be done from a wide variety of devices, such as laptops, tablets, or smartphones. This capability provides a seamless computing experience, regardless of the user’s hardware, as long as they have an internet connection. Virtual desktops are essentially virtual machines (VMs) that operate on a virtualization host, where each VM replicates a full desktop experience.
To connect to these virtual environments, users typically rely on remote desktop protocol (RDP) clients or similar software. These tools establish a secure and responsive connection to the virtual desktop, ensuring that users can interact with their environment as though it were running on a local device. This combination of centralized management, multi-user access, and remote connectivity defines the core functionality of desktop virtualization.
Types of Desktop Virtualization
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is an IT solution that enables users to access enterprise-level computer systems and resources from virtually any device. By eliminating the reliance on physical machines, VDI allows organizations to provide secure, centralized access to company servers, files, and applications. This approach ensures that employees, contractors, and partners can perform their tasks efficiently, regardless of their physical location.
VDI is particularly beneficial for supporting remote workers, branch office teams, and external collaborators. By hosting desktop operating systems on virtual machines powered by server hardware, VDI ensures consistent performance, scalability, and security. This setup simplifies IT management by centralizing the control and maintenance of desktop environments, reducing hardware costs, and improving data security through server-side storage. VDI’s ability to deliver reliable, secure, and scalable solutions makes it a cornerstone of modern enterprise computing.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
Using RDS, organizations can provide employees with remote access to desktop images and applications hosted on internal servers. The system operates via the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), ensuring secure and efficient communication between the user’s device and the centralized server. RDS is particularly well-suited for businesses seeking to enable remote access without deploying complex hardware infrastructures. Its on-premises nature makes it an attractive option for companies looking to maintain direct control over their data and IT systems while still enabling remote productivity.
Benefits of Desktop Virtualization
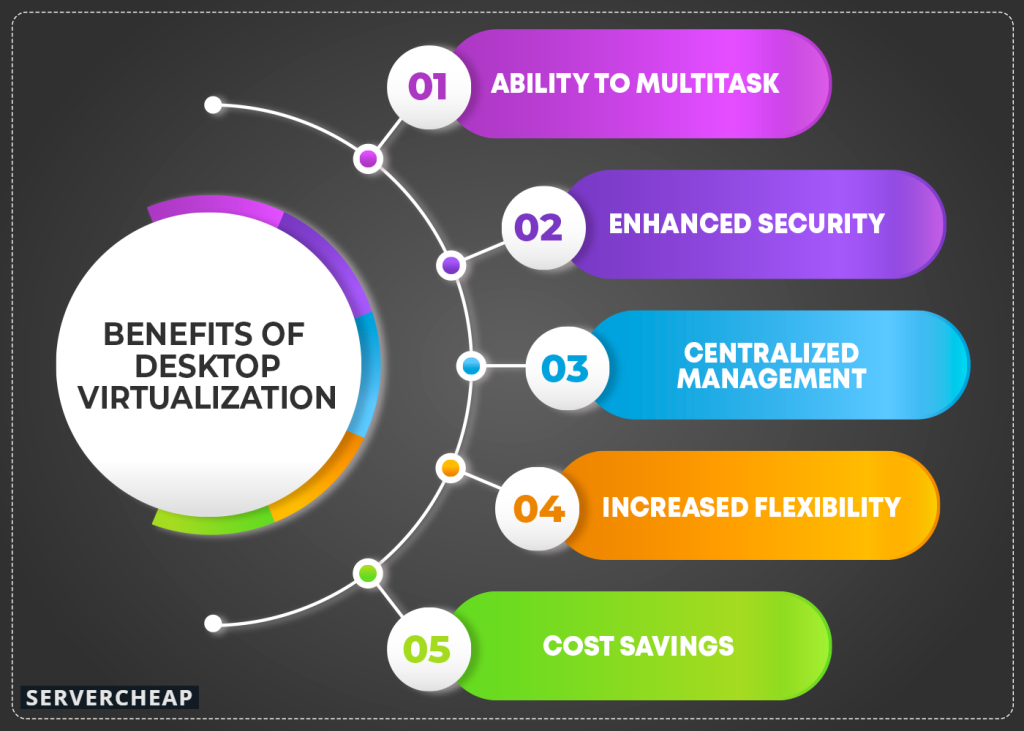
Virtual desktop technology allows users to access their work desktops from various devices, such as laptops, desktops, thin and zero clients, tablets, and even smartphones. This method offers multiple benefits:
- Ability to Multitask: Many desktop virtualization implementations allow a user to simultaneously access multiple desktops at once. Since each desktop is a separate computer machine, one may work on many computers simultaneously.
- Enhanced Security: By storing sensitive data on a central server instead of on individual devices, the risk of data theft or loss is minimized. If a device enabled with desktop virtualization is stolen, the absence of local company data significantly reduces the possibility of security breaches.
- Centralized Management: This technology simplifies the tasks of managing, updating, and configuring desktop images, applications, and user settings, all from a centralized location. It particularly aids IT administrators in maintaining oversight and control over the desktop environments of remote workers, streamlining the deployment of resources across various devices within the organization.
- Increased Flexibility: Virtual desktops can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility supports remote work and “bring your own device” (BYOD) policies, allowing users greater flexibility in how and where they work.
- Cost Savings: Organizations can lower hardware expenses by prolonging the service life of existing equipment and reducing energy costs. Desktop virtualization also reduces the need for frequent hardware upgrades.
- Stronger Security Measures: In a virtual desktop infrastructure, the desktop environment is separated from the physical hardware, which is used merely to access the virtual setup. The virtual machines delivering these desktops operate in a controlled environment, managed diligently by the enterprise’s IT department, adding an extra layer of security.
Use Cases for Desktop Virtualization
Desktop virtualization has a wide range of applications across various industries and use cases:
- Remote Work: Providing remote workers with secure and reliable access to their desktops and applications from any location .
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD): Allowing employees to use their personal devices for work while maintaining security and control over corporate data .
- Task-Based Workers: Providing temporary workers or contractors with access to specific applications and resources without the need for dedicated physical machines .
- Software Development and Testing: Creating isolated environments for developers and testers to code, test, and debug software without affecting the production environment . For example, developers can use virtual desktops to test their applications on different operating systems or configurations without having to install them on their physical machines.
- Healthcare: Enabling secure access to patient records and medical applications from any location, improving efficiency and patient care . This allows doctors and nurses to access patient information from any device, whether they are in the hospital, at a clinic, or working remotely.
- Education: Providing students with access to virtual labs and software applications, regardless of their device or location . This can be particularly beneficial for online learning or for students who need access to specialized software that may not be available on their personal devices.
- Call Centers: Offering a standardized and secure desktop environment for call center agents, ensuring consistent service delivery and data protection. This can help improve call center efficiency and reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Improved Security and Productivity: In a real-world example, an accounting firm shifted to virtual desktops housed on a centralized server in a secure data center . This improved their overall data security and reduced the risk of data breaches. Additionally, desktop virtualization increased productivity by allowing employees to access their desktops and applications from any approved device.
Choosing a Deployment Model
Selecting the right deployment model is an important step for organizations implementing desktop virtualization. The primary decision revolves around whether to adopt an on-premises Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) platform or subscribe to a cloud-based Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS) provider. Each model comes with distinct advantages and considerations, making the choice dependent on an organization’s specific needs and resources.
An on-premises VDI platform is well-suited for organizations with existing server hardware or the budget to invest in necessary infrastructure. This approach provides greater control over the environment and data, making it ideal for businesses with strict compliance or security requirements. However, it also demands significant IT expertise and resources to manage and maintain the system.
On the other hand, cloud-based DaaS is an appealing option for organizations lacking the technical expertise or budget to support an on-premises deployment. With DaaS, the responsibility for managing the infrastructure lies with the service provider, reducing the burden on internal IT teams. This model also offers scalability, allowing organizations to adjust resources as their needs evolve. Ultimately, the decision between on-premises VDI and cloud-based DaaS depends on the organization’s priorities, technical capabilities, and budgetary constraints.
Remote Desktop Virtualization
Remote desktop virtualization allows users to operate systems and applications hosted in a secure datacenter while interacting with them on their personal devices. This approach ensures that critical software and sensitive data remain protected within the organization’s infrastructure, even as users access them remotely. By centralizing resources, IT teams can maintain tighter control over security and system management, reducing vulnerabilities and simplifying maintenance.
A key benefit of remote desktop virtualization is its ability to extend the value of existing hardware investments. Organizations can provide users with access to pooled computing resources, maximizing the efficiency of server power without requiring individual high-performance machines. This cost-effective model supports remote and hybrid work environments, enabling employees to access their virtual desktops from virtually anywhere. By bridging the gap between physical limitations and digital flexibility, remote desktop virtualization is a cornerstone of modern workplace efficiency.
Major Players in the Desktop Virtualization Industry
The desktop virtualization market is competitive, with several key players offering a range of solutions and services. Some of the major players include:
| Company | Products/Services |
|---|---|
| Citrix Systems | Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, Citrix DaaS |
| VMware | VMware Horizon, VMware Workspace ONE |
| Microsoft | Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop, Windows 365 |
| Amazon Web Services | Amazon WorkSpaces |
| Cisco Systems | Cisco Virtualization Experience Infrastructure (VXI) |
| Nutanix | Nutanix Frame |
| Parallels | Parallels RAS |
Size and Growth of the Desktop Virtualization Industry
The desktop virtualization market is experiencing significant growth, driven by factors such as the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the rise of remote work, and the growing need for enhanced data security.
The global desktop virtualization market size was valued at USD 22.63 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 27.61 billion in 2024 to USD 142.66 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 22.8% during the forecast period. North America dominated the global market with a share of 35.09% in 2023.
Source: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/desktop-virtualization-market-107810
Several factors contribute to this growth:
- Increased adoption of cloud computing: Cloud-based desktop virtualization solutions offer greater scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-premises solutions.
- Rise of remote work: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work, leading to increased demand for desktop virtualization solutions that enable secure and reliable access to corporate resources from any location . The pandemic influenced the desktop virtualization market, causing the demand for virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) to grow by over 70% .
According to an article published by Anunta Tech, in September 2021, the COVID-19 pandemic influenced the desktop virtualization market, causing the demand for virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) to grow by over 70% during the period.
Source: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/desktop-virtualization-market-A18446
- Enhanced data security: Desktop virtualization enhances data security by centralizing data storage and management, reducing the risk of data loss or theft.
- Cost savings: Desktop virtualization can help organizations reduce IT costs by extending the lifespan of existing hardware, reducing energy consumption, and simplifying IT management .
Furthermore, the adoption of desktop virtualization varies across different organization sizes. Large enterprises have shown greater adoption compared to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), primarily due to the associated benefits such as improved data security and enhanced employee efficiency .
Advanced Desktop Virtualization Functionalities
GPU Passthrough and vDGA
Advanced desktop virtualization functionalities like GPU passthrough and virtual Dedicated Graphics Acceleration (vDGA) are critical for environments requiring high-performance graphics capabilities. GPU passthrough allows virtual machines (VMs) to directly access a physical GPU, granting the VM full control over the graphics card’s resources. This ensures that users experience the same level of performance and responsiveness as they would on a physical machine.
These functionalities are particularly valuable for graphics-intensive applications such as 3D modeling, video editing, and scientific simulations. By leveraging GPU passthrough or vDGA, organizations can provide power users with the tools they need without compromising performance or user experience. This capability is essential for industries where precision and graphical fidelity are non-negotiable.
Workspace Aggregation
Workspace aggregation takes desktop virtualization a step further by unifying virtual applications, desktops, and data into a single, cohesive user interface (UI). This functionality simplifies the user experience by offering seamless access to all necessary resources, regardless of the device or location. Users no longer need to navigate multiple platforms or interfaces, as workspace aggregation consolidates everything into one intuitive dashboard.
This approach enhances productivity by streamlining workflows and ensuring consistent user experiences (UX) across devices. Whether employees are accessing their workspace from a desktop at the office or a tablet on the go, workspace aggregation ensures they can quickly and easily find the tools and information they need. For organizations prioritizing simplicity and efficiency, this functionality represents a significant leap forward in digital workspace management.
Overcoming the Top Challenges of Virtualization
Network and Storage Considerations
A well-optimized network is required for successful virtual desktop deployment. It ensures smooth data transfer between virtual desktops, applications, and storage, minimizing latency and disruptions that can hamper user experience. Designing a robust network infrastructure is critical to achieving these outcomes, as it supports the bandwidth, reliability, and scalability required for virtual environments. Key factors in network optimization include sufficient bandwidth, low latency, and strategic load balancing. Without a solid foundation, even the most advanced desktop virtualization solutions may struggle to perform effectively.
Security and Compliance
As cybercrimes and data breaches continue to escalate, security remains a primary concern for virtualized environments. The shared nature of these environments often introduces unique vulnerabilities, making robust security measures indispensable. Implementing encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access controls are just a few of the steps organizations can take to safeguard their systems. Compliance with industry-specific regulations also plays a critical role in securing sensitive data, ensuring that virtual desktop solutions meet legal and ethical standards. Preparing for future security challenges requires proactive planning and the adoption of technologies designed to detect and prevent emerging threats.
Best Practices for Implementing Desktop Virtualization
Successful implementation of desktop virtualization begins with a thorough assessment of your organization’s expertise, resources, and specific needs. Whether you opt for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), Remote Desktop Services (RDS), or Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS), the choice should align with your internal capabilities and strategic objectives. Each option offers distinct benefits: VDI provides control over infrastructure, RDS is ideal for lightweight, session-based needs, and DaaS offers scalable, cloud-based flexibility.
Cost considerations, infrastructure control, and provider comparison are key factors in selecting the right solution. Organizations should weigh the upfront investment of on-premises systems against the subscription-based models of cloud services. By carefully analyzing these variables, you can ensure your desktop virtualization solution delivers both technical efficiency and financial value.
Future Trends in Desktop Virtualization
The future of desktop virtualization is poised to transform how businesses operate and innovate. Breakthroughs in high-performance hardware and networking are driving these changes, making desktop virtualization more accessible and powerful than ever. Edge Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (Edge VDI) is an emerging trend that decentralizes computing by placing virtual desktop resources closer to end users, reducing latency and improving performance for real-time applications.
Another groundbreaking development is the integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) into desktop virtualization. These technologies promise to redefine collaboration, training, and productivity, enabling immersive experiences in virtual workspaces. As these advancements gain traction, desktop virtualization will continue to evolve, offering businesses new opportunities to grow and adapt in an increasingly digital world.
We offer virtual machines based on the KVM virtualization technology with NVMe drives at low rates. To view our VM inventory with NVMe drives and order a VM, visit our VPS Ordering Page. ServerCheap VPS come with a 7-day money back guarantee.
Conclusion
Desktop virtualization allows individuals to access a computer which is located remotely but in a way as if they were sitting right in front of it. Users make this connection via the internet. It allows users to access their desktops and applications from any device with an internet connection, while also providing IT administrators with greater control over data and security. The market is driven by the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the rise of remote work, and the growing need for enhanced data security. It provides a centralized infrastructure that hosts a desktop image that users can access remotely.
Since the data and applications reside on servers rather than individual devices, desktop virtualization can enhance security. Managing multiple operating system instances becomes simpler with desktop virtualization. IT administrators can deploy, manage, and update these instances centrally, rather than having to handle each user’s machine individually. This central management is especially beneficial in large organizations.
